Material Selection
Hard Materials: which is right for me?

Clockwise from left: silicon carbide, stainless steel , tungsten carbide, aluminum oxide
oxide — are so different from other engineering materials and from each other that an informed understanding of these properties is necessary in order to maximize their use. Each of the materials is extremely hard, falling just below diamond on the hardness scale. Corrosion resistance, transverse rupture strength, fracture toughness and weight vary greatly. Let’s look at some of the key characteristics of each material.
Silicon Carbide exists in two forms: reaction bonded and alpha sintered (or self-bonded).
Reaction bonded silicon carbide is formed when powdered silicon carbide reacts with free carbon and molten silicon. The material does not shrink during the reaction process, which allows for near net forming of components. Silicon is present on the surface, which reduces friction in dynamic applications. It is the material of choice for high speed and pressure applications. However, the silicon also limits the upper use temperature to 2100° F and can be attacked by hydrofluoric acid and other caustics like alkalis and halogens. They are commonly used for mechanical seal faces.
Alpha sintered (or self-sintered) is excellent for components requiring exceptional wear and corrosion resistance at temperatures up to 2500° F. It is extremely hard and lightweight with virtually no porosity. Components produced with alpha sintered silicon carbide are harder than those made from tungsten carbide or oxide ceramics, and more than 50 percent lighter. Since there is no free silicon or other binder material, the material exhibits excellent corrosion resistance compared to tungsten carbide, oxide ceramics, or reaction bonded silicon carbide. This is a workhorse material that can be applied in a variety of applications such as mechanical seals, bushings, bearings and shafts in applications like chemical processing, refining, paper and pulp, food and beverage, marine and waste water.
Tungsten Carbide, also known as cemented tungsten carbide, is a terrific candidate for applications where hardness, wear and rigidity are of importance. There are many grades available which have considerable variations in their properties. Indicative of a material with “cemented” in its name, cemented tungsten carbide exhibits extremely high compressive strength which is several times its tensile strength. Binder content and material, most commonly cobalt and nickel, can be modified to increase corrosion resistance, wear resistance and fracture toughness. The most common application for tungsten carbide is as a tool for metal forming. Common industrial applications are mechanical seal faces, spray nozzles, seats and balls.
Oxide Ceramics are the most widely used and are generally the lowest cost of the hard materials. They come in various formulations which can affect specific mechanical properties. One key characteristic is that they exhibit excellent abrasion and corrosion resistance while maintaining their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. They do not perform well in applications where there is impact. Typical applications are bushings, electronic insulators, nozzles and sleeves.
In summary, the essence of hard material characteristics is their ability to perform admirably in extreme applications. The severity of the application specifics determines which properties are most desirable and, in turn, the optimum hard material for your application.
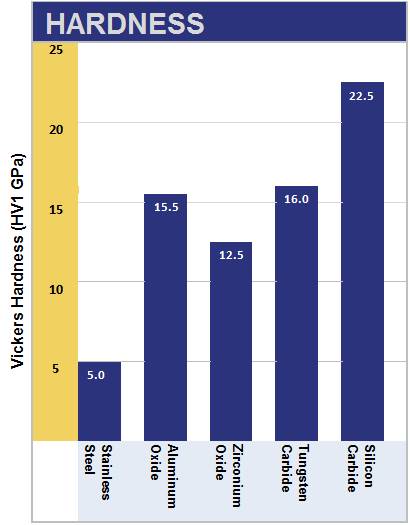
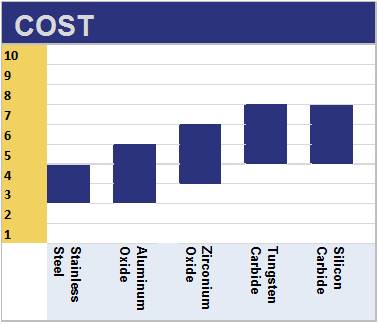
Note that there are many factors influencing the price of a component, including grades of material, forming and firing processes, as well as geometry and tolerances.
At JJISCO, Inc. we take great pride in our material-centric approach to enhancing your equipment. JJISCO is a strong participant in many diverse, extreme and intensive markets that demand materials which will not only hold up to corrosion, heat and wear, but will also excel. The key is knowing which one to choose for your specific application.
Watch for an upcoming issue that directly compares the mechanical properties and costs, and takes a more in-depth look at these materials. If you have questions or have a current need, please contact us directly for assistance with your specific application.
The information included in this article is for guideline purposes only. We recommend each application be tested for its specific intended use. Please contact JJISCO technical support for more in-depth discussions on your unique program, including cost-effective design.

